-
Original Article
- Multi-Method Assessment of Inter-rater Reliability in Dental Implant Stability Measurements
- Min-Ju Gu, Seok-Hyeon Kim, Yun-Gyu Yang, Hyeong-Seok Oh, Hae-Rin Jeong, Dong-Woo Heo, Jung-Bo Huh
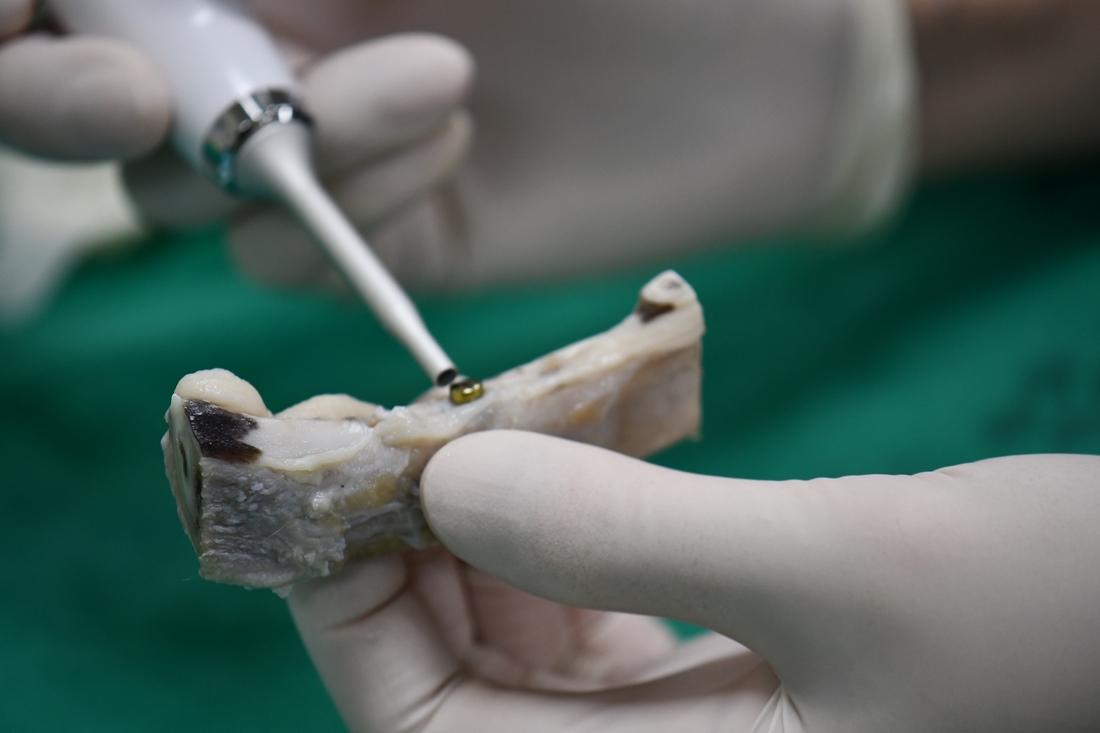
- Purpose: Implant stability is a critical determinant of successful osseointegration. Common assessment methods include percussion testing, resonance frequency analysis, radiographic evaluation of …
- Purpose: Implant stability is a critical determinant of successful osseointegration. Common assessment methods include percussion testing, resonance frequency analysis, radiographic evaluation of marginal bone levels, and histometric analysis. Although many studies have assessed the reliability of individual methods, few have examined their concordance when applied by different examiners. This study aimed to evaluate the reproducibility of widely accepted implant stability measurement techniques by comparing results obtained by researchers who received identical training. Materials and Methods: Five junior researchers from a dental school assessed the stability of implants placed in one beagle. The methods included Implant Stability Quotient (ISQ), Implant Stability Value (ISV), radiographic analysis, and histologic analysis—specifically, bone-to-implant contact (BIC) and interthread bone density (ITBD). Interrater reliability was calculated using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) with a 95% confidence interval. Results: All methods demonstrated statistically significant reliability (p < .05). BIC (ICC = 0.806) and ITBD (ICC = 0.854) exhibited high to very high reliability. ISQ (ICC = 0.774) and radiographic analysis (ICC = 0.638) showed moderate to high reliability. ISV (ICC = 0.447) exhibited low reliability. Conclusion: BIC, ITBD, ISQ, and radiographic analysis demonstrated consistent reproducibility among trained examiners, with BIC and ITBD showing particularly high concordance. ISV measurements were comparatively less reliable. Within the limitations of this study—including a small sample size, the use of a single animal model, and limited measurement repetitions—histometric parameters demonstrated the strongest interrater agreement. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Article
- Accuracy of Tooth-Supported Surgical Guides According to the Number of Supporting Teeth in Dental Implant Placement
- Chan-Young Lee, Taek-Geun Jun, Jin-Hyuk Kwon, Sang-Hoon Kang
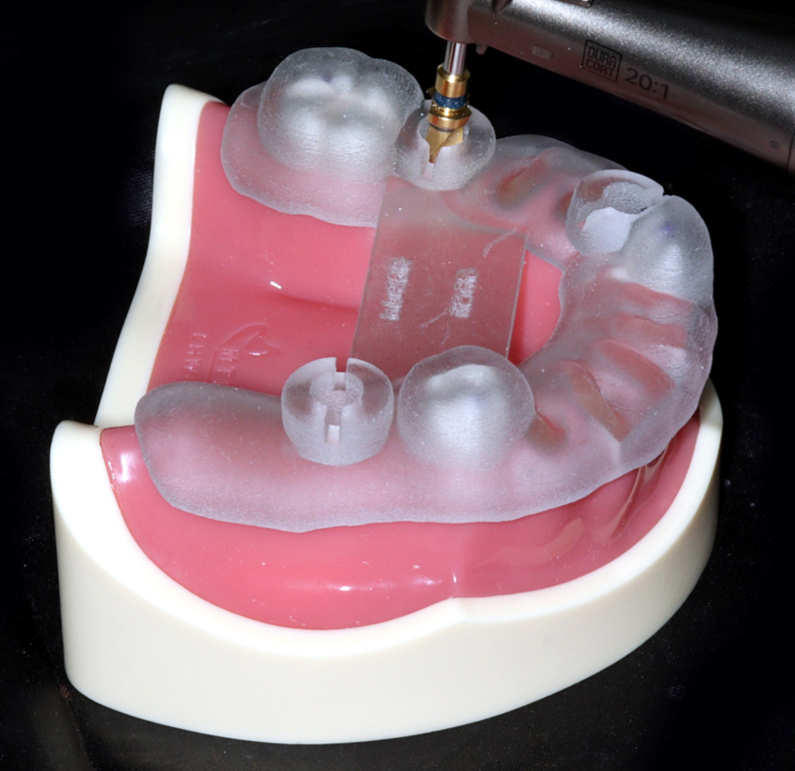
- Purpose: This study evaluated the accuracy of computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM)-fabricated stereolithographic surgical guides according to the number of supporting teeth …
- Purpose: This study evaluated the accuracy of computer-aided design and manufacturing (CAD/CAM)-fabricated stereolithographic surgical guides according to the number of supporting teeth in patients with partial edentulism undergoing implant placement.Materials and Methods: The experimental group consisted of maxillary and mandibular arches with only three remaining teeth per arch arranged in a triangular distribution (anterior, left posterior, and right posterior) without adjacent contacts. The control group comprised arches with seven or more remaining teeth per arch, allowing adjacent contacts. Implant placement was performed at edentulous sites, with three implant sites designated per maxillary and mandibular model, using CAD/CAM-fabricated surgical guides.Results: No statistically significant differences were observed between the groups with respect to distance and angular errors. When evaluating the minimum distance between the two central axes, the mean error was 0.16 ± 0.17 mm for guides supported by seven or more teeth and 0.20 ± 0.12 mm for guides supported by three teeth. When assessing the angular deviation of the implant axis, the mean error was 3.02 ± 2.05° in the group with guides supported by seven or more teeth and 3.41 ± 2.64° in the group with guides supported by three teeth.Conclusion: This in vitro study demonstrated that using tooth-supported CAD/CAM surgical guides for implant placement in partially edentulous cases with only three remaining teeth resulted in no significant deviations. This study provides a basis for the application of digital implant surgical guides in clinical practice, particularly in cases with limited remaining teeth for support. - COLLAPSE
-
Original Article
- Effect of Prosthesis Materials and Cementation Techniques on Stress Distribution in Implant Fixtures
- Ji-Hoon Jang, Yoon-Jeong Shin, Cheong-Hee Lee
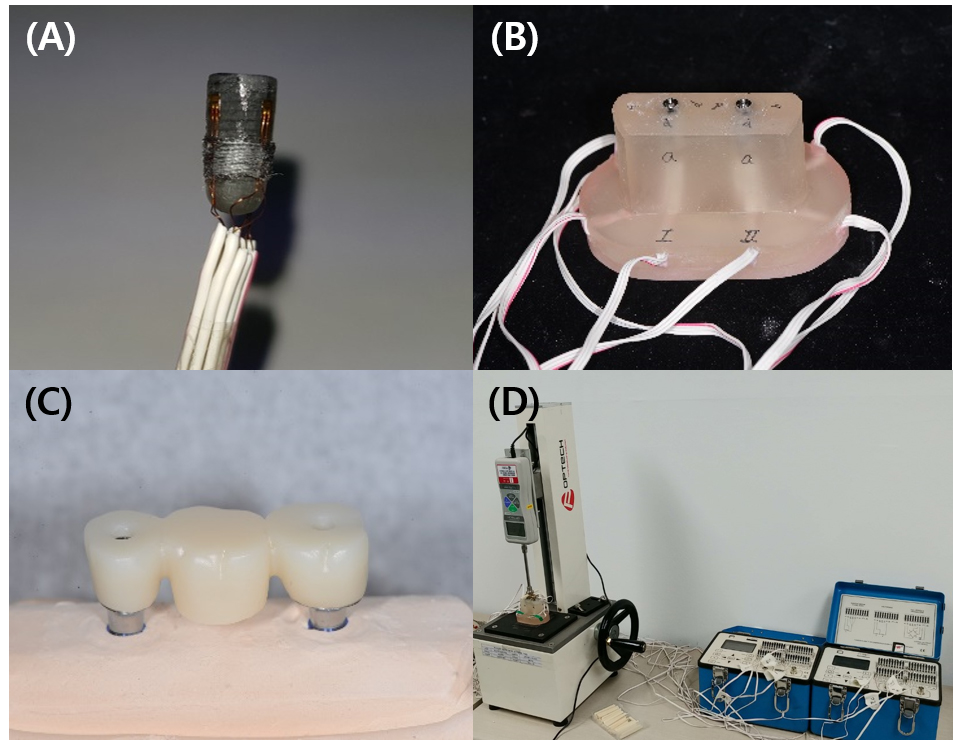
- Purpose: This study aimed to measure the stress generated in implant fixtures based on the material used in three-unit fixed prostheses with …
- Purpose: This study aimed to measure the stress generated in implant fixtures based on the material used in three-unit fixed prostheses with implants, utilizing strain gauges for cementation methods, and to conduct a comparative analysis.Materials and Methods: Three-unit implant-supported fixed prosthesis models were fabricated with two internal-connection implants placed in the mandibular left second premolar and second molar positions. Four strain gauges were attached to the cervical area of each implant fixture. A conventional cement-retained group (Co) and screw-cement-retained prosthesis (SCRP) groups using non-precious metal (Me), precious metal (Go), and zirconia (Zi) were prepared. In the SCRP groups, the abutments were tightened to either 10 or 30 Ncm before cementation and finally fixed at 30 Ncm. Cementation was performed under one- or two-point loading. Strain values were measured 10 min after cementation and final tightening. Absolute strain values were analyzed using independent t-tests for group comparisons.Results: No significant differences were observed between one- and two-point loading in any group (p > .05). Significantly higher strain values were detected in the 10 Ncm SCRP groups than in the 30 Ncm SCRP and conventional cement-retained groups (p < .05). No significant differences were observed between the prosthesis materials.Conclusion: In SCRP restorations using internal-connection implants, mismatched abutment tightening torque before and after cementation may induce increased stress around implant fixtures, whereas the prosthesis material and loading point have no significant influence. - COLLAPSE
-
Clinical or Case Report
- An Implant Finder Service for Restoring Undocumented Implants: A Case Series
- Dong Neong Huh, Sung-Jo Lee, Yu Imai
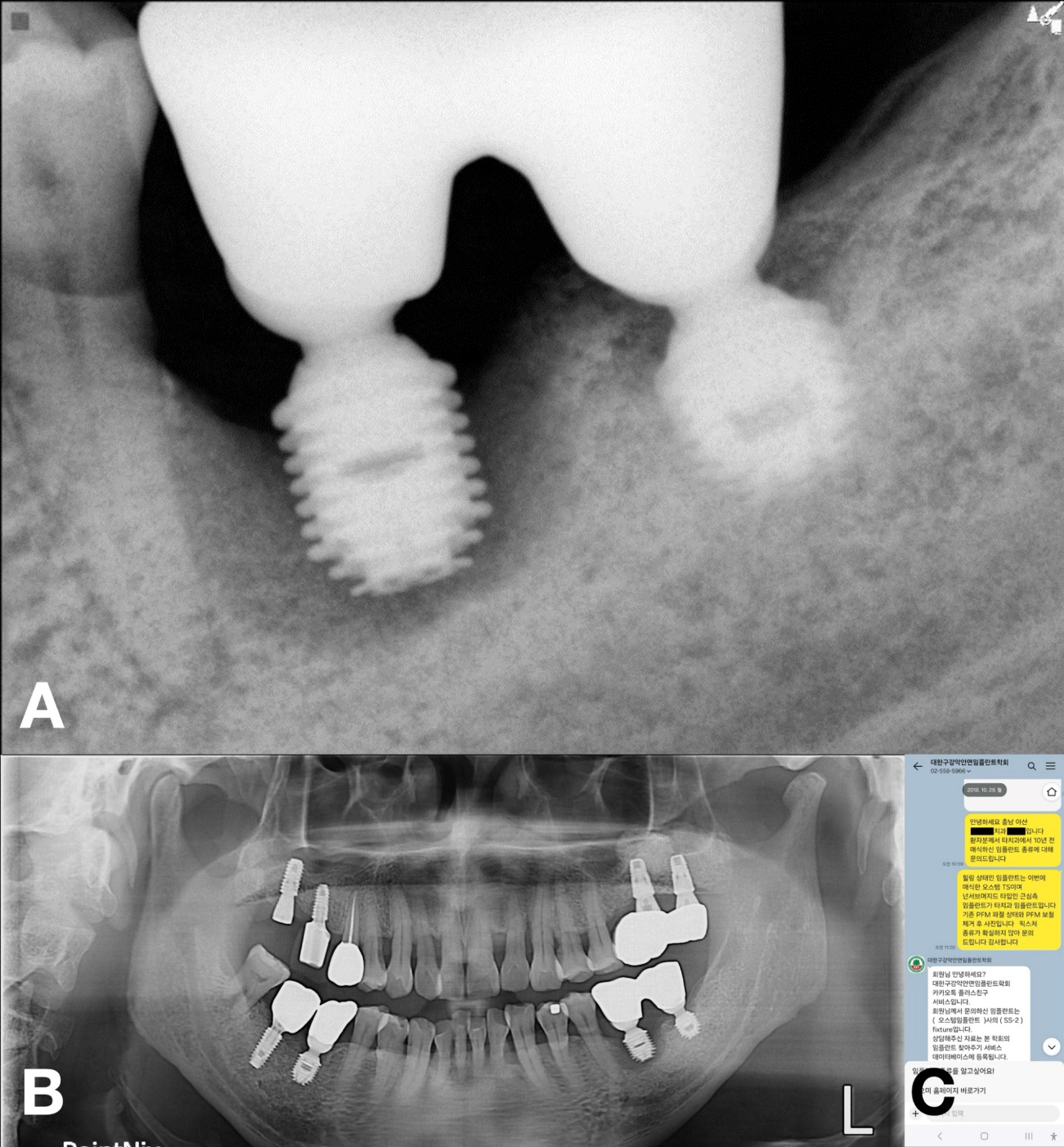
- Clinicians frequently encounter implants with undocumented histories that necessitate prosthetic revision. This report describes two cases of multi-implant restorations for undocumented implants, …
- Clinicians frequently encounter implants with undocumented histories that necessitate prosthetic revision. This report describes two cases of multi-implant restorations for undocumented implants, facilitated by an implant finder service. In both cases, existing prostheses were nonfunctional. The Korean Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Implantology implant finder service accurately identified the unknown implant systems, providing specifications for compatible components, enabling reuse of fixtures that might otherwise have required removal. This approach preserved existing structures and enhanced patient comfort. The restorations demonstrated successful function over follow-up periods of 2.5 and 6 years, respectively. Given the diagnostic challenges posed by radiographic limitations and the wide variety of implant systems, implant finder services represent an invaluable tool for clinicians. - COLLAPSE
-
Clinical or Case Report
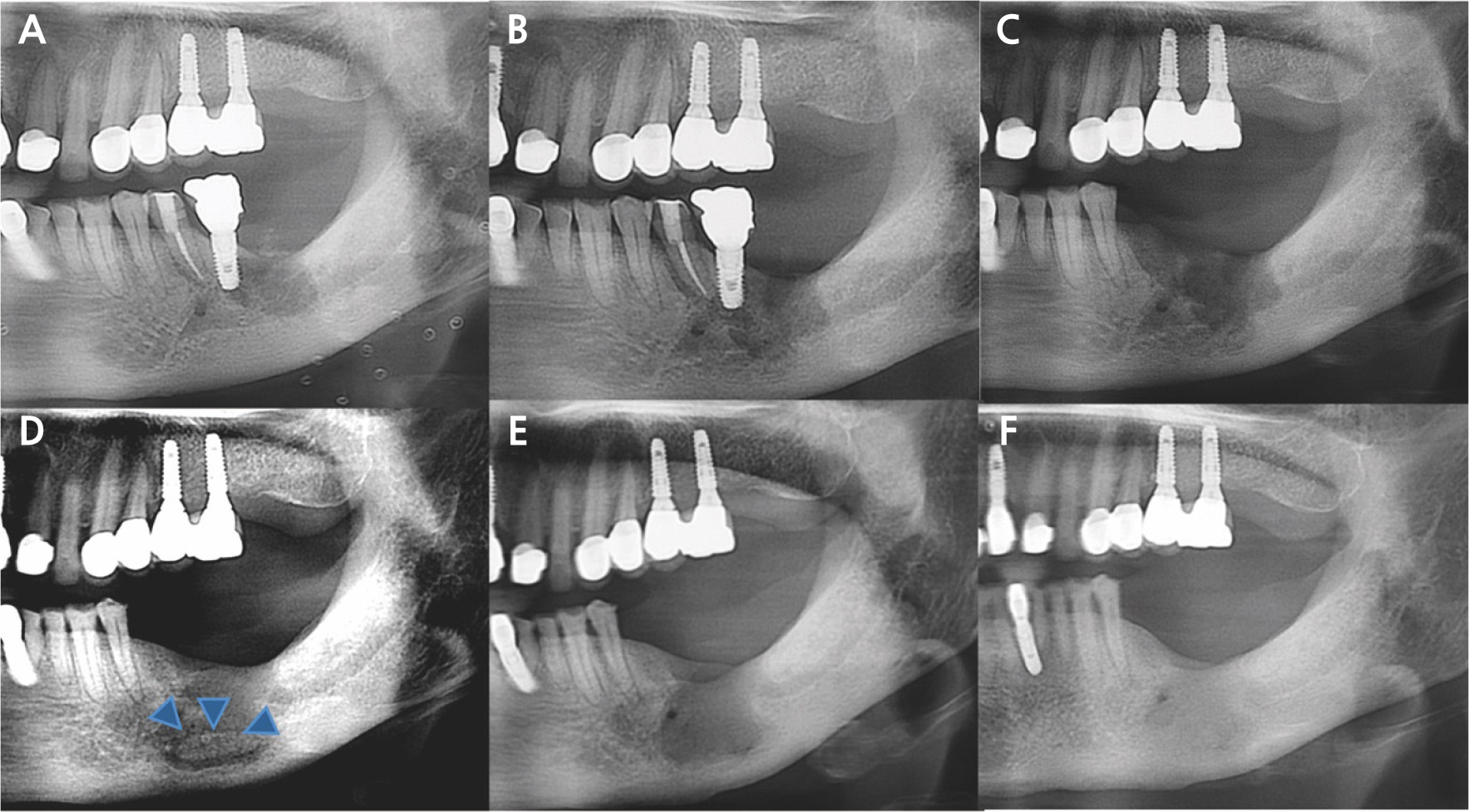
- Development of Medication-related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Associated with Dental Implant: Report of Two Cases
- Yongjun Cho, Seung Tae Kim, Hye-Sun Kim, Jong-Ki Huh, Reuben H. Kim, Jae-Young Kim
- Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) is a known complication of antiresorptive therapy. Although its pathogenesis remains unclear, several studies have reported …
- Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (MRONJ) is a known complication of antiresorptive therapy. Although its pathogenesis remains unclear, several studies have reported MRONJ development around osseointegrated implants. This study presents two cases of implant-associated MRONJ and discusses the relevant risk factors and management approaches. The first case involved a 68-year-old woman who had been receiving oral bisphosphonate therapy for approximately 6 years and presented with persistent pain around mandibular implants without any notable evidence of bone destruction. Despite multiple conservative and surgical interventions, the symptoms persisted. Complete mucosal healing was achieved after removal of the adjacent tooth and sequestrectomy with reimplantation. The second case involved a 72-year-old woman who developed MRONJ around implants in multiple regions. She had been receiving bisphosphonate and corticosteroid therapy. Repeated sequestrectomies and implant removals were required to control the disease, followed by successful healing of the mandibular lesions. Clinicians should inform patients that MRONJ can develop even around osseointegrated implants. Furthermore, MRONJ development should be considered in patients undergoing antiresorptive treatment for osteoporosis who present with atypical symptoms around dental implants. - COLLAPSE
-
Clinical or Case Report
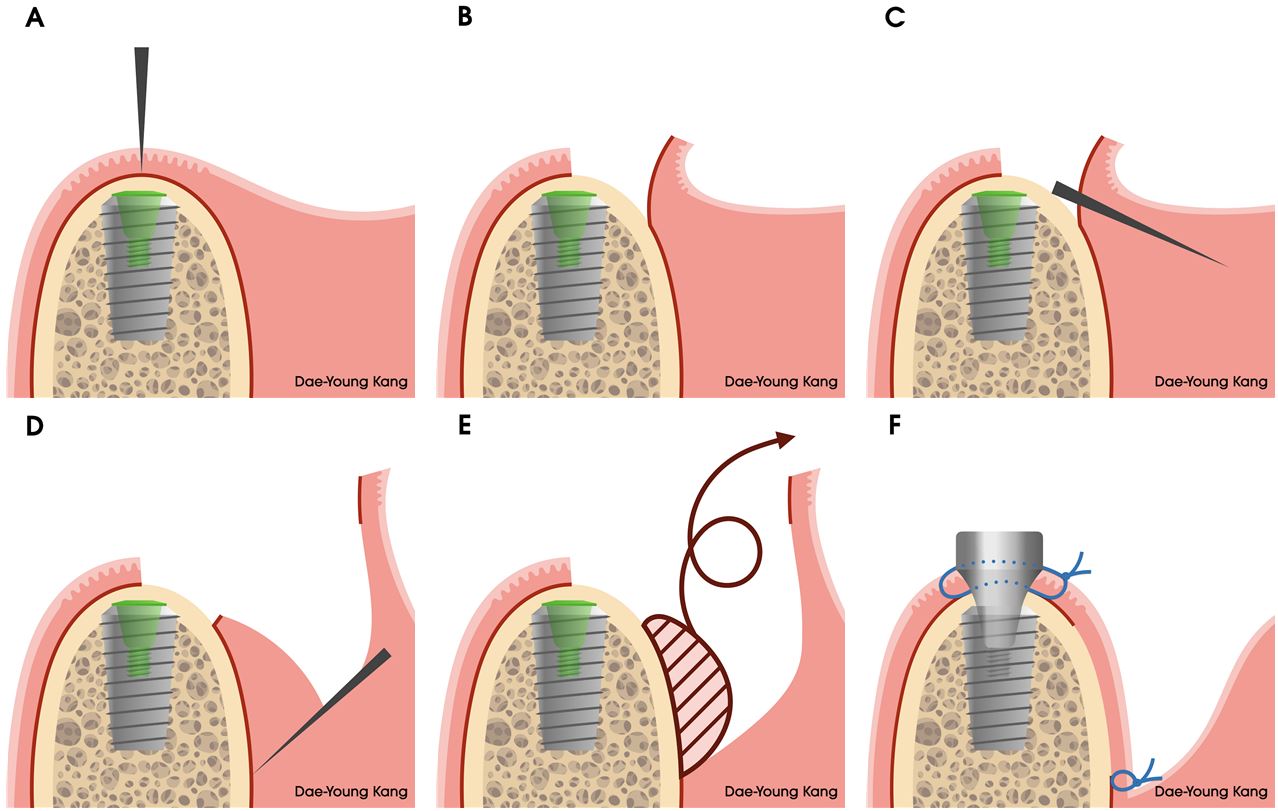
- Technical Note on the Modified Submucosal Vestibuloplasty Around Dental Implants: A Case Report
- Sung-Jo Lee, Dae-Young Kang, Hyeon-Seong Ahn, In-Woo Cho
- Shallow vestibular depth with inadequate attached mucosa around dental implants can compromise peri-implant health and maintenance. This technical note describes a modified …
- Shallow vestibular depth with inadequate attached mucosa around dental implants can compromise peri-implant health and maintenance. This technical note describes a modified submucosal vestibuloplasty technique performed during second-stage implant surgery and demonstrates its clinical application. A 65-year-old woman received multiple implants in the bilateral posterior mandible with simultaneous guided bone regeneration. After a four-month healing period, second-stage surgery was performed using the modified technique. A midcrestal incision was made, followed by full-thickness flap elevation to expose the implant. The apical portion of the flap was then elevated as a superficial split-thickness flap, and the deeper connective tissue and periosteum were removed. Healing abutments were placed, and double horizontal mattress sutures were used to anchor the flap at the most apical level of the vestibule. The technique successfully restored vestibular depth and produced non-keratinized yet clinically attached mucosa with minimal morbidity. Compared with conventional approaches, such as an apically positioned flap with free gingival grafting or the Edlan–Mejchar technique, this modified approach offers greater simplicity and may reduce technique sensitivity and postoperative complications. However, long-term follow-up and histologic evaluation are required to confirm the stability of the newly formed vestibule and attached mucosa. - COLLAPSE
Journal Informaiton
 Journal of implantology and applied sciences
Journal of implantology and applied sciences
Journal Informaiton
Journal Informaiton - close
 Journal of implantology and applied sciences
Journal of implantology and applied sciences













